China is reinforcing its military relationships with Tanzania and Mozambique by participating in a trilateral counterterrorism drill called “Peace Unity-2024.” This exercise highlights China’s comprehensive approach to military diplomacy, which blends military operations with political, diplomatic, cultural, and commercial interactions.
Key Components
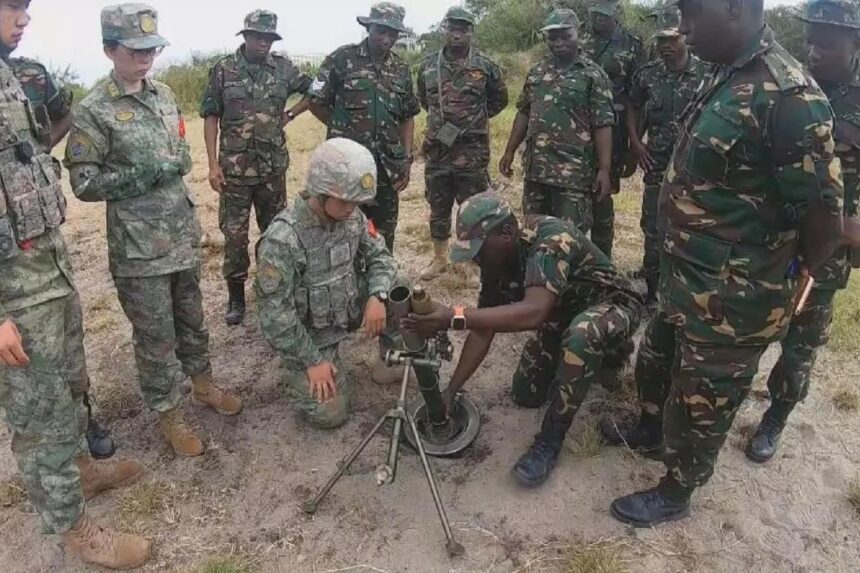
Battlefield and Tactical Training: The “Peace Unity-2024” drill involves a variety of military activities, including battlefield assessments, command post setups, and tactical training with armored vehicles and artillery. Maritime operations will also be a significant component, featuring boarding exercises, anti-piracy patrols, and joint sea patrols.
Chinese Military Participation: China has dispatched ground forces from the PLA Central Theatre Command and a naval fleet from the Southern Theatre Command to participate in the drill. The naval contingent includes the guided-missile destroyer Hefei and the amphibious dock landing ships Qilianshan and Wuzhishan.
Strategic Objectives: The exercise aims to enhance the military capabilities of the participating nations while strengthening political relationships between China and the African nations. It aligns with China’s Maritime Silk Road interests and promotes stability in the Western Indian Ocean region.
Cultural and Public Engagement: Beyond military operations, the Chinese contingent plans to engage in cultural events and public activities, such as vessel open days. These efforts are part of China’s broader military and cultural diplomatic strategy.
Broader Implications
Experts suggest that this collaborative drill will yield multiple advantages for both China and the participating African nations. It exemplifies China’s broader strategy to fortify political, commercial, ideological, cultural, and defense connections, while enhancing its global standing among African nations. The “Peace Unity-2024” drill is a clear demonstration of China’s commitment to integrating military diplomacy with its overall foreign policy objectives.
Fresh Approach to International Diplomacy
China is redefining its approach to international diplomacy, employing a multifaceted strategy that integrates military operations with political, diplomatic, cultural, and commercial interactions. This “blended approach” reflects a shift towards more comprehensive and strategic engagements on the global stage, particularly in regions like Africa and the Asia-Pacific.
Key Elements of China’s Diplomatic Strategy
Military Diplomacy: China has been increasingly using its military capabilities to foster international relations. Joint military exercises, such as the recent “Peace Unity-2024” drill with Tanzania and Mozambique, demonstrate China’s commitment to building stronger defense ties. These exercises not only enhance military capabilities but also promote stability and security in strategic regions.
Economic and Commercial Ties: Through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China is investing heavily in infrastructure, trade, and economic development projects worldwide. This not only boosts economic ties but also strengthens political relationships. For instance, infrastructure projects in Africa and Asia have cemented China’s role as a crucial development partner.
Cultural Diplomacy: China is leveraging cultural exchanges to build soft power. This includes cultural events, educational exchanges, and the promotion of Chinese language and culture through Confucius Institutes globally. By engaging in cultural diplomacy, China aims to foster goodwill and mutual understanding.
Technological Collaboration: China is fostering technological partnerships with various countries, particularly in areas like telecommunications, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy. By sharing technology and expertise, China is positioning itself as a leader in innovation and sustainable development.
Political Engagement: China’s diplomatic efforts include active participation in international organizations and multilateral forums. By playing a proactive role in the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and other global institutions, China seeks to influence international policies and promote a multipolar world order.
Recent Examples of China’s Diplomatic Initiatives
“Peace Unity-2024” Drill: The trilateral counterterrorism drill with Tanzania and Mozambique is a clear example of China’s blended approach. The exercise not only involved military operations but also included cultural events and public engagement activities, demonstrating the integration of military and cultural diplomacy.
Belt and Road Initiative: China’s investment in infrastructure projects across Asia, Africa, and Europe under the BRI has significantly boosted its economic and political influence. These projects range from building ports and railways to developing energy infrastructure, all aimed at enhancing connectivity and economic integration.
COVID-19 Vaccine Diplomacy: During the COVID-19 pandemic, China’s distribution of vaccines to various countries, particularly in the Global South, showcased its commitment to global health and solidarity. This move also helped strengthen China’s diplomatic ties and improve its international image.
Strategic Goals
Enhancing Global Influence: China’s multifaceted diplomacy aims to enhance its global influence and establish itself as a major player on the world stage. By integrating military, economic, cultural, and technological efforts, China seeks to build a network of strategic partnerships.
Promoting Stability and Security: Through military exercises and defense cooperation, China aims to promote regional stability and security. This is particularly evident in its engagements in the Asia-Pacific and African regions, where security challenges are prevalent.
Fostering Economic Growth: By investing in infrastructure and technological collaborations, China is fostering economic growth both domestically and internationally. These efforts are designed to create a more interconnected and prosperous global economy.
Building Soft Power: Cultural diplomacy and international cooperation in education and technology are key components of China’s strategy to build soft power. By promoting Chinese culture and fostering mutual understanding, China aims to create a positive global image.
China’s fresh approach to international diplomacy, characterized by its blended strategy, is reshaping global interactions and positioning the country as a central figure in international relations. This comprehensive approach not only enhances China’s influence but also contributes to global stability and development.
ALSO READ: China and Saudi Arabia rapidly expand military co-operation













Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.