In today’s interconnected world, the role of multilateral development banks in driving global economic growth has never been more crucial. One such key player is the New Development Bank (NDB), formerly known as the BRICS Development Bank, which was established by the BRICS nations—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—to foster sustainable development through strategic financial support. As this bank continues to evolve, it has emerged as a trusted partner for both public and private projects, offering loans, guarantees, and equity participation to bolster international development efforts. For journalists and policymakers keen on understanding its impact, the NDB represents a pivotal force in reshaping how international finance can address pressing economic challenges. Join us as we delve deeper into how the New Development Bank is making its mark on the global stage and explore the opportunities it presents for businesses and economies worldwide.
The Role of the New Development Bank
The New Development Bank (NDB) plays a crucial role in shaping global economic development. This section explores the bank’s history, foundation, and its core mission and objectives.
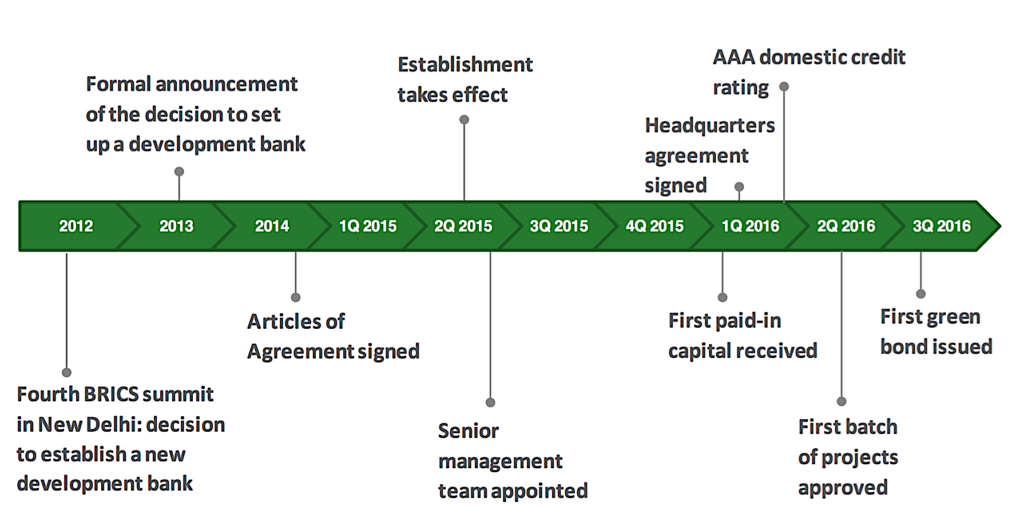
History and Foundation of NDB
The New Development Bank, initially known as the BRICS Development Bank, was established in 2014 by the BRICS nations: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. This landmark decision came after years of discussions amongst these emerging economies about creating an alternative to existing international financial institutions.
The formation of the NDB was driven by a desire to address the growing infrastructure and sustainable development needs of emerging markets and developing countries. The founding members recognized the limitations of existing multilateral development banks in meeting these needs.
With its headquarters in Shanghai, China, the NDB officially began operations in 2015. The bank’s initial focus was on infrastructure and sustainable development projects within BRICS countries, but it has since expanded its scope to include other emerging economies and developing nations.
Mission and Objectives
The New Development Bank’s primary mission is to mobilise resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS countries and other emerging economies. This mission is guided by several key objectives that shape the bank’s operations and strategy.
One of the NDB’s main goals is to complement existing efforts of multilateral and regional financial institutions in global growth and development. The bank aims to foster greater financial and development cooperation among BRICS nations and other emerging markets.
According to research, the NDB also strives to promote innovation and flexibility in its approach to development financing. This includes exploring new financial instruments and adapting to the changing needs of member countries and global economic conditions.

Financial Instruments and Services
The New Development Bank offers a range of financial instruments and services to support its mission of fostering sustainable development. This section delves into the bank’s primary financial tools: loans, guarantees, and equity participation.
Loans and Guarantees
The New Development Bank provides a variety of loan products to support infrastructure and sustainable development projects. These loans are tailored to meet the specific needs of member countries and project requirements.
NDB offers both sovereign and non-sovereign loans. Sovereign loans are extended to member governments or government-backed entities, while non-sovereign loans are available to private sector companies and financial institutions.
The bank also provides loan guarantees, which can help borrowers access funding from other sources by reducing the risk for potential lenders. This instrument is particularly useful for projects that might otherwise struggle to secure financing due to perceived risks.
Equity Participation
Equity participation is another key financial instrument offered by the New Development Bank. Through this mechanism, the NDB can directly invest in projects or companies, becoming a shareholder and sharing in both the risks and potential returns.
This approach allows the NDB to support projects that may not be suitable for traditional loan financing. It can be particularly effective for innovative or high-risk ventures that have the potential for significant developmental impact.
Studies have shown that equity participation can also help attract additional private sector investment, as the NDB’s involvement can serve as a signal of project viability and reduce perceived risks for other investors.
Impact on Global Development
The New Development Bank has made significant strides in contributing to global development since its inception. This section examines the bank’s impact on economic growth and its collaboration with member nations.
Contributions to Economic Growth
The New Development Bank has played a crucial role in driving economic growth across its member nations and beyond. By financing key infrastructure and sustainable development projects, the NDB has helped create jobs, improve living standards, and boost economic productivity.
One of the bank’s notable achievements has been its focus on renewable energy projects. These investments not only contribute to sustainable development but also help member countries transition to cleaner energy sources, reducing their carbon footprint.
Research from Boston University highlights that the NDB’s approach to development financing has been particularly effective in addressing gaps left by traditional multilateral development banks, especially in sectors like sustainable infrastructure and digital technology.
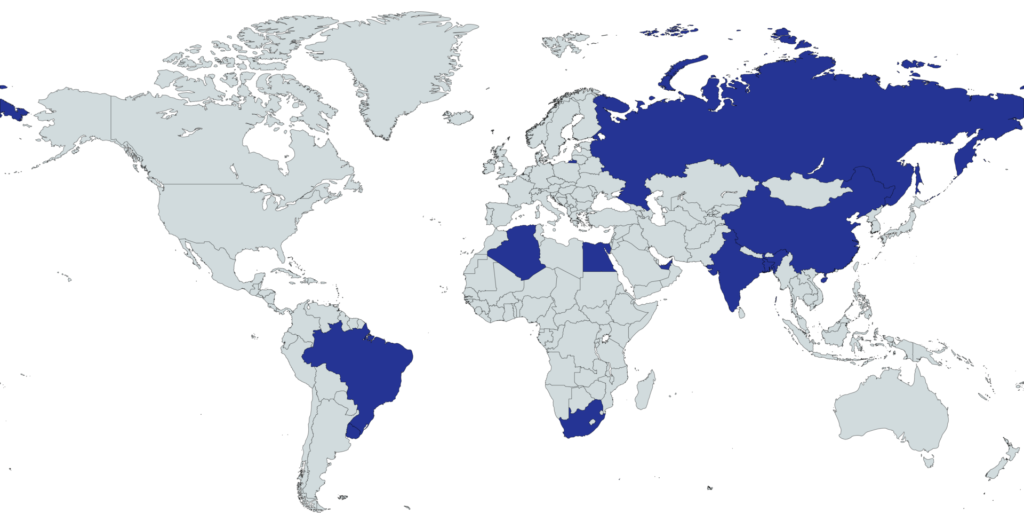
Collaboration with Member Nations
The New Development Bank’s success is largely due to its strong collaboration with member nations. This partnership approach ensures that the bank’s activities are aligned with national development priorities and strategies.
NDB works closely with governments, local financial institutions, and private sector entities in member countries to identify and develop projects. This collaborative approach helps ensure that projects are tailored to local needs and conditions.
The bank also facilitates knowledge sharing amongst member nations, promoting the exchange of best practices and innovative solutions to common development challenges. This aspect of NDB’s work contributes to building capacity and expertise within member countries, fostering long-term sustainable development.













